Do you ever feel lost in a sea of acronyms and technical jargons every time you look at a smartphone spec sheet? Fear not, dear reader, for this article will serve as your trusty guide to all things YugaSpecs.
From acronyms to units of measurement, we’ll break down the key features and terminologies you need to know in order to make an informed decision when choosing your next smartphone.

Now to give an explainer, we categorized the various features listed in smartphone spec sheet into different groups such as Display, Processor and Configuration, Cameras, and Build.
This categorization will help you better understand the information listed in a spec sheet and allows for easier comparison between different smartphone models.
Table of Contents

The image above is a sample spec sheet of the Nothing Phone (1). How many of these information do you know? No worries, we’re going to cover them all, and now let’s move along with the guide.
Kicking off with one of the most important parameters to consider in a smartphone, the display—that’s why this is always the first one in our spec sheet.

A. Display size – the physical size of the screen in inches that is measured diagonally in full rectangle.
B. Screen resolution – refers to the number of pixels on the screen described with its base name like “FHD+” then followed by its format, usually expressed as width x height pixels.
The higher the resolution, the more detailed and clear the image will appear on the screen. For example, a smartphone display with a resolution of 1080 x 2400 pixels will have more pixels than a screen with a resolution of 720 x 1520 pixels, resulting in a sharper image with more detail. Screen resolutions are often categorized into different types, such as HD, Full HD, and 4K.
C. Display technology – this is the type of display panel used.
One of the most common types of display technology for smartphones is AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode). This type of display uses organic compounds that emit light in response to an electric current. AMOLED displays tend to have better color accuracy, deeper blacks, and faster refresh rates than other types of displays like LCD (Liquid Crystal Display). They also tend to consume less power than LCD displays, as they only illuminate the pixels that need to be lit up, resulting in better battery life.
However, AMOLED displays can be more expensive to produce than LCD displays, which may result in higher prices for smartphones that use them.
On top of those display panels are their particular type of backplane technology such as, LPTO (seen in OLED displays), IPS and TFT (in LCD displays).
Backplane technology refers to the type of technology used in the substrate of a display panel. This technology can affect the performance of the display, including factors such as power consumption, response time, and image quality.
LPTO or Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide is a type of display technology that is commonly used in smartwatches and some high-end smartphones. LPTO displays are known for their energy efficiency, as they can dynamically adjust the refresh rate based on the content being displayed, resulting in longer battery life.
While IPS stands for In-Plane Switching and is a type of LCD technology that is commonly used in smartphones and other devices. IPS displays offer good color accuracy and wide viewing angles, making them a popular choice for mobile devices.
And TFT is an acronym for Thin Film Transistor and is a type of LCD display technology that is commonly used in older smartphones and other devices. TFT displays are known for their fast response times and low power consumption, but they are not as energy efficient as newer display technologies like LPTO.
D. Refresh rate – refers to the number of times per second the screen is updated, usually expressed in Hz.
A higher refresh rate means that the screen can display more images per second, resulting in smoother animations and transitions. For example, a 120Hz refresh rate means that the screen is updated 120 times per second. This results to a more responsive and enjoyable user experience, especially when playing games or watching videos with fast-moving action. However, a higher refresh rate can also consume more battery life, so it is important to balance performance with battery efficiency.
E. Aspect ratio – is the proportional relationship between the width and height of a display screen. It is expressed as a ratio of the width to the height, such as 16:9 or in the sample, 20:9. The aspect ratio can affect the overall size and shape of the phone, as well as your viewing experience. Thus, if a phone has a higher aspect ratio, black bars can be seen from the sides when watching videos with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
F. Pixels per inch – also abbreviated as ‘PPI’ (or ‘ppi’ is most cases) is a measure of the pixel density of a display, usually in reference to a smartphone screen. A higher PPI means that there are more pixels packed into each inch of the screen, resulting in a sharper, more detailed image.
RELEVANT READ: Caught in 4K: A Comprehensive Guide to Display Resolutions
G. Touch sampling rate – refers to how often the screen detects touches, usually expressed in Hz too.
A higher touch sampling rate means that the screen can detect touches more quickly and accurately, which can lead to a smoother and more responsive user experience. However, it is worth noting that touch sampling rate is just one factor in overall screen responsiveness, and a higher refresh rate can also contribute to a more responsive display.
H. Display protection – this is a thin layer of glass onto a display and acts as an added protection from scratches and accidental drops. The most popular being the Gorilla Glass manufactured by Corning; there’s the Kunlun Glass developed by Huawei; and the Dragontrail glass by Asahi India Glass (AIS).
I. Nit – is a unit of measurement used to describe the brightness of a display. The higher the number of nits, the brighter the display can get. A display with a higher number of nits can be easier to see in bright sunlight or other high-ambient light environments. In general, a display with a brightness of at least 400 nits is considered bright enough for most indoor and outdoor viewing conditions. High-end smartphones can have displays with brightness levels of up to 1000 nits or more.
The next set of parameters is also crucial in smartphones. You don’t want to really get a device that performs lowly to your expectations, do you?
Well, out there, you may run into budget or entry-level smartphones that use low-end processors. There are also midrange phones that are equipped with potent processors at a significantly lower price than the flagship phones. And speaking of flagships, these are certainly the ones that are equipped with the high-end processors.
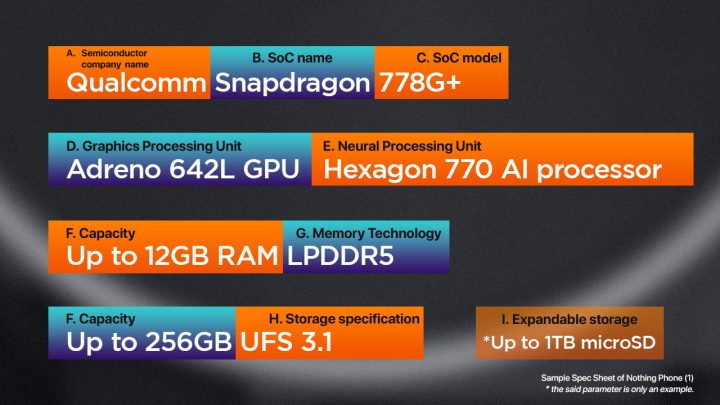
A. Semiconductor company name – refers to the company that provides the chipset, such as Qualcomm or MediaTek.
Apart from Qualcomm and MediaTek, there are other semiconductor companies that manufacture chipsets for smartphones.
Some of these include Samsung who produces the Exynos chipset; of course, Apple with the A-series Bionic chipset for iPhones; Huawei who produces the Kirin chipset for Huawei (and Honor smartphones), and Intel with the Atom chipset for some Android devices.
Each of these chipsets has its own strengths and weaknesses, and it’s worth researching which chipset a particular smartphone model uses before making your own purchase.
B. System-on-chip (SoC) name – It is called system on a chip for a reason. It integrates all the major components of a smartphone, including the CPU, GPU, modem, and memory controller all in a single chip. It is designed to maximize performance and efficiency while minimizing power consumption.
The SoC name refers to the specific family of chips produced by a particular semiconductor company, such as Snapdragon by Qualcomm or Dimensity by MediaTek. With each SoC having its own unique set of features, performance capabilities, and power consumption profiles.
C. SoC model – describes the specific version of the chip within a particular family, such as the most powerful ones yet, the Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 or the Dimensity 9200, and of course, Apple’s own silicon, the Apple A15 Bionic chip. The model number generally indicates the level of performance and capabilities of the chip, with higher numbers indicating more advanced features.
Some examples of mid-range smartphone chips include the Qualcomm Snapdragon 778G, the MediaTek Dimensity 1100, and the Samsung Exynos 1080. These chips offer solid performance at a more affordable price point than flagship-level chips.
While entry-level smartphone chips include the Qualcomm Snapdragon 400 and 600 series, the MediaTek Helio A and P series, and even the unfamiliar ones like Unisoc Tiger and JLQ. These chips offer basic performance on a budget.
Apple also has its own chipset for its Mac laptop and desktop computers including the latest Apple M2.
D. Graphics processing unit (GPU) name – we sometimes exclude this since the SoC is usually tied with a specific GPU, but for the benefit of this guide, it deserves an explanation. GPU is an important component of the SoC that is responsible for rendering graphics and images on the smartphone’s display. Different SoCs use different GPU designs, such as Adreno by Qualcomm or Mali by ARM.
E. Neural Processing Unit (NPU) name – abbreviated as NPU, which is a specialized processing unit designed to perform machine learning tasks. NPUs are used in smartphones to accelerate tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing. They work by using algorithms and neural networks to analyze data and make predictions based on that data. By offloading these tasks to an NPU, smartphones can perform these tasks more quickly and with less power consumption than if they were performed by the main processor or GPU. However, not all smartphones have an NPU, and they tend to be found in higher-end models.
F. Capacity – refers to the amount of RAM and storage, usually expressed in gigabytes (GB). But certain phones have achieved 1TB when it comes to internal storage.
To further elaborate, here’s a brief explainer: Bytes, kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB) are units of measurement used to describe the amount of data stored on a device or even transferred over a network.
G. Memory technology and extended RAM – pertains to the type of RAM used in a smartphone. LPDDR5 is the latest and most advanced type of RAM available in smartphones. It offers faster performance and lower power consumption compared to LPDDR4X.
Some smartphones also have extended RAM which utilizes the phone’s internal storage as additional RAM. This can help improve performance in certain situations, but it is not as fast as dedicated RAM and may not be available on all devices.
H. Storage specification – the type of storage used in a smartphone. UFS (Universal Flash Storage) is the current standard for high-speed internal storage in smartphones. UFS 4.0 is the latest storage spec with over 4200MB/s sequential read and up to 2800MB/s sequential write—making it so much faster than UFS 3.1 with 2100MB/s read and 1200MB/s write. And miles ahead from eMMC 5.1 with 250MB/s read and 125MB/s write.
I. Expandable storage – Some smartphones also have expandable storage, which allows users to insert a microSD card to increase the phone’s storage capacity. However, not all smartphones have this feature and it usually not be available on higher-end models.
Huawei also has its own expandable storage system called NMcard, which stands for Nano Memory Card. It is smaller than a microSD card but offers the same functionality and is applied in some Huawei and Honor smartphones.
Aside from the previous parameters, this one is probably the most important for the average consumer.
No need to deny it, we all wanna look good in our photos and videos using our phones. And since every smartphone today (even the entry-level ones) has cameras, a bit of knowledge about this topic may help you decide which unit to go for.

A. Megapixel count – describes the number of pixels in the camera sensor. A higher megapixel count generally means that the camera can capture more detail in each shot. However, megapixels are not the only factor to consider when evaluating camera quality. Other factors, such as the size and quality of the camera lens, the type of sensor used, and the software processing used to enhance images, can all have a significant impact on image quality.
For example, a camera with a higher megapixel count may not necessarily produce better images if the lens is of low quality or the software processing is not optimized. Additionally, higher megapixel counts can result in larger file sizes, which can take up more storage space on a device.
B. Aperture or f-stop – refers to the size of the camera lens opening, which controls how much light enters the camera.
This also works the same with DSLR cameras. A lower f-stop number means a larger lens opening, which allows more light into the camera and results in a brighter image. A higher f-stop number means a smaller lens opening, which allows less light into the camera and results in a darker image. The aperture also affects the depth of field, which is the area of the image that appears in focus. A larger aperture (lower f-stop number) results in a shallower depth of field, with only the subject in focus and the background blurred. A smaller aperture (higher f-stop number) results in a deeper depth of field, with both the subject and background in focus.
C. Type of sensor/ lens – the type of camera sensor or lens used. Our spec sheet, by default, mention how many cameras a certain smartphone has.
Usually in smartphone cameras, there’s the main lens or the primary lens used for taking photos or videos. It has the widest aperture and typically has the highest megapixel count. The ultrawide lens, on the other hand, has a wider field of view and is used to capture more of the scene in a single shot. The macro lens is used for taking close-up shots of small objects, while the depth sensor is used to capture depth information and create a bokeh effect in portrait mode. Lastly, the telephoto lens is used for zooming in on distant objects, and it has a longer focal length than the main lens.
D. Smartphone sensor manufacturer – smartphone brands may also disclose where they got the camera sensors for their products, such as Sony and Samsung sensors—two of the largest manufacturers of camera sensors for smartphones.
Sony is known for producing high-quality camera sensors for many flagship smartphones, including the Google Pixel, OnePlus, and Sony’s own Xperia phones. Samsung also produces camera sensors for its own smartphones, as well as for other smartphone manufacturers. Samsung’s ISOCELL sensor technology is used in many high-end smartphones, including the Galaxy S series.
Both Sony and Samsung continue to innovate and develop new camera sensor technologies, such as larger sensor sizes, improved low-light performance, and faster autofocus. The choice between Sony and Samsung sensors often depends on the specific smartphone model and the preferences of the manufacturer.
Our spec sheet also determines Optical Image Stabilization (OIS) and Electronic Image Stabilization (EIS) if a device has it. These are two different technologies used to reduce camera shake and improve image stabilization.
OIS works by using a gyroscope to detect camera shake and adjusting the lens accordingly to compensate for the movement. This results in a more stable image and can be particularly useful in low-light situations or when taking photos with a slow shutter speed.
EIS works by using software algorithms to compensate for camera shake. It works by cropping the edges of the frame and then digitally stabilizing the remaining image. While EIS can be effective in reducing camera shake, it can also result in a loss of image quality and a smaller field of view.
E. Camera system tuning – Leica, Hasselblad, and Zeiss are well-known lens manufacturers that have collaborated with smartphone companies to produce high-quality camera systems for their devices. These partnerships allow smartphone manufacturers to leverage the expertise of these established camera companies to craft camera systems that can compete with dedicated point-and-shoot cameras.
Leica has collaborated with Huawei on several smartphone models, including the P30 Pro and Mate 30 Pro. The Leica-branded camera systems on these devices feature advanced zoom capabilities and low-light performance. Leica, however, is now collaborating with Xiaomi with their latest collab output, the Xiaomi 13 Pro.
Hasselblad has partnered with OnePlus on the Hasselblad-branded camera system with the latest OnePlus 11. This camera system features a custom sensor and lens setup that is optimized for low-light performance and color accuracy.
Zeiss has collaborated with Nokia on several smartphone models, including the Nokia 9 PureView. This device features a unique camera system with five lenses that can capture incredibly detailed images.
This section is where we talk about the network capability of a device including its other connectivity features.
Does the phone support dual SIM? Is it 5G-enabled? USB Type-C already? For some, the absence of 5G is considered a deal breaker. And yeah, don’t even mention the micro-USB hate.
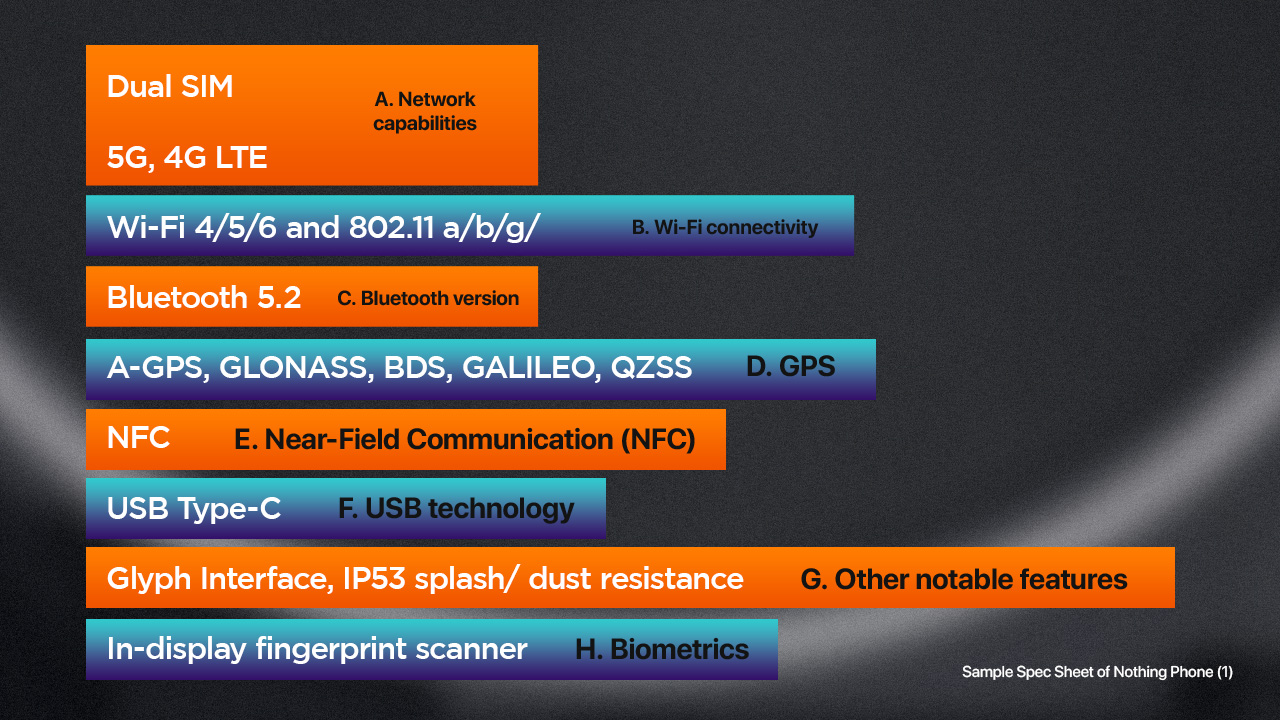
A. Network capabilities – refers to the supported network technologies, such as 5G or 4G LTE. We also mention if it’s dual SIM (even though most Android phones nowadays support it) or single SIM like Apple.
B. WiFi connectivity – is the device’s supported WiFi standard, such as WiFi 6—a recent Wi-Fi standard that offers faster speeds and greater network efficiency. It can support up to 9.6 Gbps of data transfer speed and is also known as 802.11ax. Wi-Fi 5, also known as 802.11ac, is the previous Wi-Fi standard and can support up to 3.5 Gbps of data transfer speed. It is still a popular Wi-Fi standard, but it is not as fast as Wi-Fi 6.
C. Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless communication technology used to connect devices over short distances. It is used for a variety of purposes, such as connecting wireless headphones or speakers to a smartphone, transferring files between devices, and connecting to IoT devices like smart home appliances. Bluetooth works by using radio waves to establish a connection between two devices. The range of Bluetooth varies depending on the version of Bluetooth used and the environment, but it typically ranges from a few meters to tens of meters.
The latest Bluetooth version is Bluetooth 5.3.
D. Global Positioning System (GPS) sensors – refers to the supported GPS technology. There are several different GPS technologies used in smartphones, including A-GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO, BDS, and QZSS. A-GPS, or Assisted GPS, uses data from cellular networks to improve GPS accuracy and speed up the time it takes to acquire a GPS signal. GLONASS is a Russian satellite navigation system that is similar to GPS. GALILEO is a European satellite navigation system that offers global coverage. BDS, or BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, is a Chinese satellite navigation system. QZSS, or Quasi-Zenith Satellite System, is a Japanese satellite-based augmentation system that is designed to improve GPS accuracy in urban environments.
E. Near-Field Communication (NFC) – allows devices to communicate wirelessly over short distances. NFC is often used for contactless payments, where a user can simply tap their phone to a payment terminal to make a purchase. It can also be used for transferring files, connecting to wireless devices like headphones or speakers, and accessing information from NFC tags like Apple’s Air Tags.
NFC works by using electromagnetic induction to establish a connection between two devices. One device acts as the transmitter, while the other acts as the receiver. When the two devices are brought close together, they create a magnetic field that allows them to communicate.
NFC is a popular feature in many smartphones because of its versatility and convenience. It is supported by many apps and services, and is often used for mobile payments and other secure transactions. However, it is worth noting that not all smartphones have NFC, so keep that in mind.
F. USB technology – refers to the supported USB standard, such as USB Type-C, which is the latest USB standard that supports fast data transfer rates, high power delivery, and versatile connectivity. There’s also Apple’s Lightning port also having an irreversible design yet not as fast as USB-C.
You can learn more about different USB standards here.
G. Other notable features – sometimes, if a phone brand disclose information like IP certification or any other protection, we also include it in the spec sheet.
IP (Ingress Protection) certification is a rating system used to describe the level of protection a device has against solid objects and liquids. It consists of two digits, with the first digit representing the level of protection against solid objects and the second digit representing the level of protection against liquids.
For example, a device with an IP68 rating is dust-tight and can be submerged in water up to a depth of 1.5 meters for up to 30 minutes. The higher the numbers, the better the protection.
If a phone has other unique features, like Nothing’s Glyph Interface or ASUS ROG Phone 6’s Aura RGB lighting or vapor chamber cooling technicalities, we also insert those aesthetic additions in this section of the spec sheet.
Additionally, infrared sensors are still utilized by smartphones and Xiaomi is often the one who implements it almost in every phone they make. An infrared sensor allows the phone to be used as a universal remote control for various household devices such as TVs, air conditioners, and sound systems.
H. Biometrics – refers to the supported biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or face recognition.
It is also specified where is the biometrics scanner is located, whether under-display which uses either optical or capacitive sensors, and on the rear or the side.
This section certainly completes the most relevant information to look for in a spec sheet. The operating system and the battery.
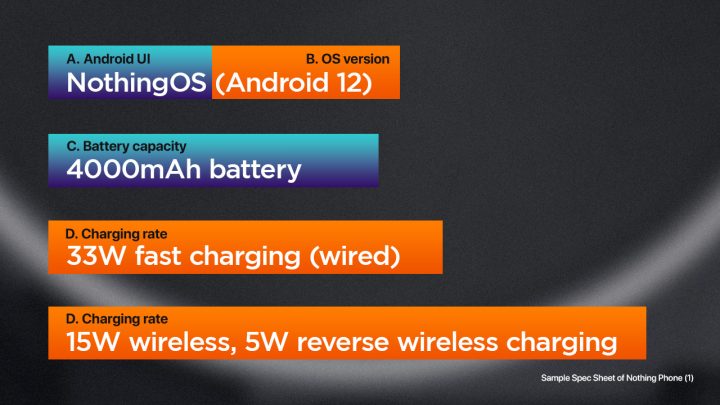
A. Android skin/ UI – are custom software overlays that smartphone manufacturers use to differentiate their devices from others running stock Android.
Popular Android skins include Samsung’s One UI, OnePlus’ OxygenOS, and Xiaomi’s MIUI. Each of these skins has its own unique design and feature set, and they can significantly alter the user experience of the device.
You may watch our video about some of the popular Android UI out there and we even picked the best one!
B. OS version – the operating system (OS) version refers to the version of the Android OS.
There have been 13 versions of Android already while Apple’s iOS is now at 16th iteration.
Previously, Google had officially given dessert names for each Android versions like the Android 8 as Oreo, 9 as Pie, until the 10th iteration in which they just called it simply, Android 10.
In every iteration of Android and iOS, we saw improvements and new features added over time. While older, outdated OS versions get thrown into oblivion since phone makers eventually drop support for them.
Android makers usually last until four years of support with Samsung leading the pack. But Apple is definitely the ‘gigachad’ of them all with up to five years of software support.
C. Battery capacity – just in case you don’t know yet, it refers to the amount of energy the battery can store, typically measured in milliampere-hours (mAh).
The higher the mAh rating, the longer the battery can last between charges. However, it’s important to note that battery life is also affected by other factors, such as the phone’s display size and resolution, the processor and graphics chip, and the user’s individual usage patterns.
D. Charging rate – is the speed at which the smartphone’s battery can be charged and is typically expressed in watts (W). A higher charging rate means that the battery can be charged more quickly, which can be useful if you need to charge your phone quickly before leaving the house or while on the go.
Most smartphones support fast charging, which allows the battery to be charged more quickly than with a standard charger. However, the maximum charging rate will depend on the specific smartphone and the type of charger being used. Some smartphones support charging rates of up to 100W, while others may only support rates of 18W or less.
Wireless charging will also be mentioned if the phone supports it. It is a novelty feature that allows a smartphone to charge without needing to be physically connected to a charger via a cable. Instead, the phone is placed on a wireless charging pad, which uses electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from the pad to the phone’s battery.
Wireless charging is a convenient way to charge a phone, as it eliminates the need for cables and can be done simply by placing the phone on the charging pad. However, wireless charging can be slower than wired charging, and the phone needs to be placed in a specific position on the charging pad to work properly.
A smartphone can also do reverse wired and wireless charging. Reverse wired charging works by connecting the smartphone to another device, such as a Bluetooth earbud case or another phone, using a USB cable. The smartphone then supplies power to the other device, charging its battery. This feature can be useful in emergency situations where another device’s battery is low and there is no power source available.
Reverse wireless charging works similarly, but instead of using a cable, the smartphone uses its wireless charging coils to transfer energy to another device. The other device must support wireless charging in order for this feature to work. Some examples of devices that can be wirelessly charged using a smartphone include wireless earbuds and smartwatches.
It’s worth noting that reverse charging can drain the smartphone’s battery quickly, so it is not recommended to use this feature frequently or for extended periods of time.
Finally, we have the build parameters of a device. This is where the spec sheet mention how thick a phone is, how heavy or light is it, and of course the colorways available.
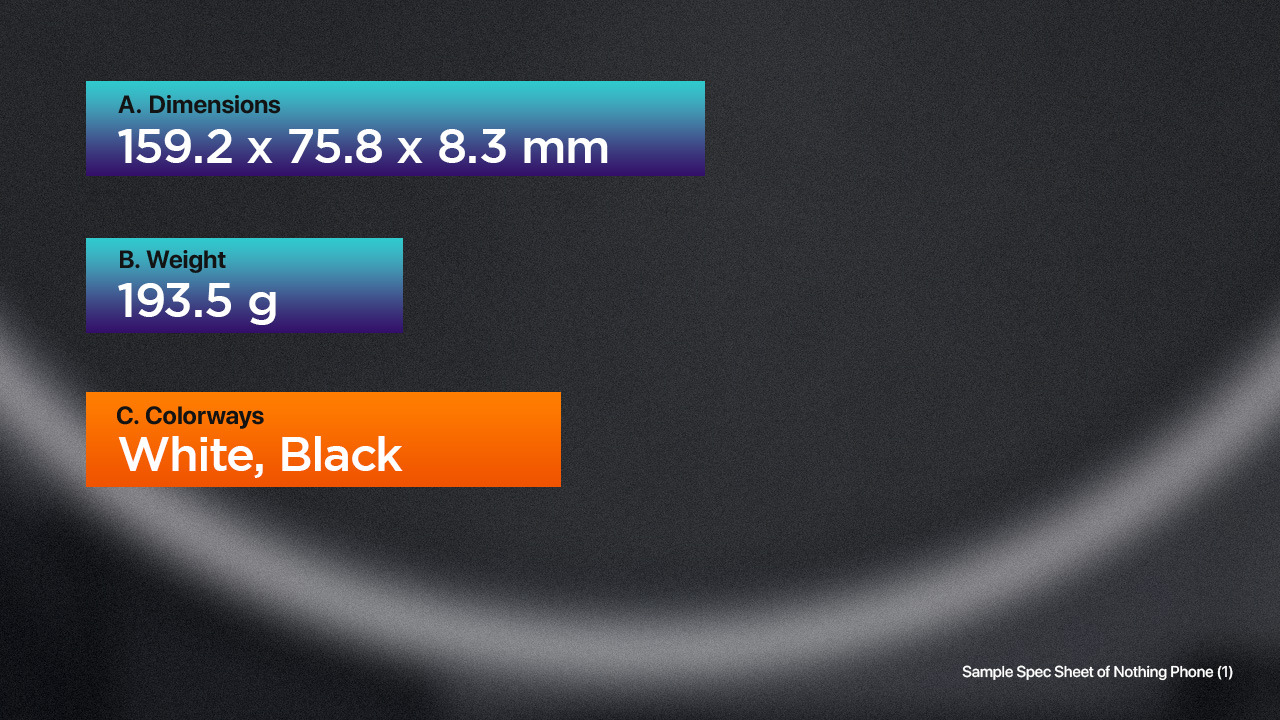
A. Dimensions (length, width, and thickness) – pretty self-explanatory but it pertains to the physical size of the phone, usually expressed in millimeters or inches using L x W x H equation.
B. Weight – refers to the weight of the phone, usually expressed in grams.
C. Colorways – are the available colors of the device. Normally, they are expressed with the phone maker’s choice of words.
Understanding smartphone specifications can be a daunting task and we hope that this guide has provided you with a better understanding of the various information listed in a smartphone spec sheet not just from ours, but on other materials out there where a spec sheet is printed like the packaging box of your phone.

YugaTech.com is the largest and longest-running technology site in the Philippines. Originally established in October 2002, the site was transformed into a full-fledged technology platform in 2005.
How to transfer, withdraw money from PayPal to GCash
Prices of Starlink satellite in the Philippines
Install Google GBox to Huawei smartphones
Pag-IBIG MP2 online application
How to check PhilHealth contributions online
How to find your SIM card serial number
Globe, PLDT, Converge, Sky: Unli fiber internet plans compared
10 biggest games in the Google Play Store
LTO periodic medical exam for 10-year licenses
Netflix codes to unlock hidden TV shows, movies
Apple, Asus, Cherry Mobile, Huawei, LG, Nokia, Oppo, Samsung, Sony, Vivo, Xiaomi, Lenovo, Infinix Mobile, Pocophone, Honor, iPhone, OnePlus, Tecno, Realme, HTC, Gionee, Kata, IQ00, Redmi, Razer, CloudFone, Motorola, Panasonic, TCL, Wiko
Best Android smartphones between PHP 20,000 - 25,000
Smartphones under PHP 10,000 in the Philippines
Smartphones under PHP 12K Philippines
Best smartphones for kids under PHP 7,000
Smartphones under PHP 15,000 in the Philippines
Best Android smartphones between PHP 15,000 - 20,000
Smartphones under PHP 20,000 in the Philippines
Most affordable 5G phones in the Philippines under PHP 20K
5G smartphones in the Philippines under PHP 16K
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2024
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2023
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2022
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2021
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2020