Ever found yourself scrambling to charge your smartphone? Well, most of us have at some point in our lives as smartphone charging 10 speeds have become an important factor in making sure our devices are always ready to keep up with our demands.
But what exactly determines how quickly your smartphone charges? Let’s dive into the details of smartphone charging speed and the factors that influence it.

Table of Contents
Smartphone charging speed refers to how quickly a smartphone’s battery can be replenished with electrical energy or charged, making it an important aspect for users who want their smartphones to charge rapidly and efficiently.

While it may seem like a straightforward concept, charging speed is influenced by several factors, including the charging technology, the charger’s output power, the battery capacity, and the software optimizations in the smartphone.
The charger you use plays a crucial role in charging speed. Chargers are rated by their output power, measured in watts (W).
Simply put, a charger with a higher wattage can deliver more power to the smartphone, resulting in faster charging times. For instance, a 30W charger will charge faster than a 10W charger.

If you want some options for some of the fastest chargers, here’s a list of some 100W chargers, best budget chargers 13, and recommended 3rd party chargers 13 all of which are great pick-ups.
Apart from the charger, you need to make sure your smartphone actually supports faster speeds. Most smartphones use various charging technologies that determine how fast they can charge. Some common modern charging technologies include:
USB Power Delivery or simply USB PD is the universal fast-charging standard that was published by the USB-IF in 2012. In 2023, most phones have supported USB PD with the use of a USB-C port.
This has been notably highlighted recently with Apple and their switch from their proprietary Lightning port to now using USB-C on their iPhone 15 lineup.

USB PD typically starts at 18 watts but can go much higher with some chargers supporting up to 100 watts or more being able to even charge tablets or laptops.
You’ll also come across the term “USB PD PPS” or “USB PD Programmable Power Supply” which allows certain smartphones to specifically program their own voltage and current levels. This is where we get to see some modern smartphones go beyond 100W charging with speeds up to 240W even.
Qualcomm’s Quick Charge is a type of fast charging technology widely used in Android smartphones that use Qualcomm’s Snapdragon processors which can charge anywhere between 18W and 120W.
There are also different versions with Quick Charge 5 being the latest and as well as being now backward compatible with all previous Quick Charge versions and USB PD.

Just note that although Quick Charge can be found on a lot of Android smartphones, but unless the charger is Quick Charge 5 compatible, both the charger and smartphone must support the same version of Quick Charge to reach its optimal charging speed.
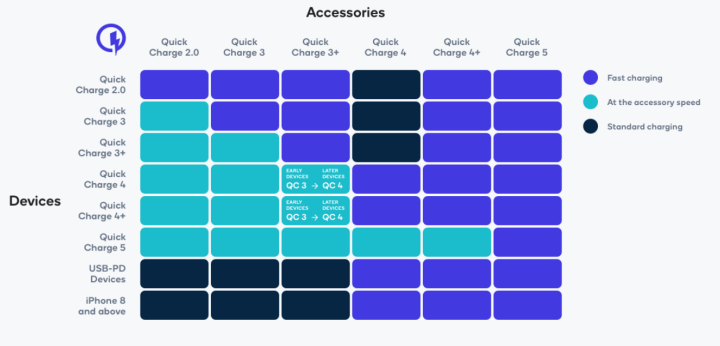
Qualcomm Quick Charge Compatibility (Devices & Accessories)
Qualcomm Quick Charge also offers various safety features like overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and temperature management to prevent overheating.
Most smartphones from flagship, mid-range, and even some budget-friendly ones commonly now offer fast charging.
However, manufacturers like OPPO (SuperVOOC), MediaTek (Pump Express), Xiaomi (HyperCharge), and Huawei (SuperCharge) have developed their own fast charging technologies that use higher voltages and currents to deliver more power to the battery, thus reducing charging time.
To know how fast charging actually works, be sure to our explainer on fast charging just above! And if you want an in-depth look at specific smartphone charging technologies, be sure to see our guide on it.

Qi wireless charging is a technology that allows devices to charge without plugging in a cable. While convenient, wireless charging can be slower compared to wired fast charging.

Most standard wireless chargers can typically provide 5 to 10 watts while some more advanced wireless chargers can go up to 30W.
But today in 2023, what is normally seen amongst most smartphones is the ability to wirelessly charge at 15W.
The size of the smartphone’s battery, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh) or watt-hours (Wh), directly affects how long it takes to charge.
A larger battery will take longer to charge compared to a smaller one, considering that both are charged with the same charging speed in watts.

Over time, a smartphone’s battery capacity may degrade, leading to slower charging speeds.
Some modern smartphones have battery management systems that can adjust charging speed to prolong battery life.

Manufacturers often implement software features to optimize charging speed and safety.
These features include temperature monitoring to prevent overheating, adjusting charging speed based on the battery’s state of charge, and optimizing power usage during charging.
The quality of the charging adapter and cable matters too. A poor-quality cable might not be able to handle high currents effectively, leading to slower charging speeds.
For the most part, you want to make sure that your charging adapter and cable both support the fast speeds you need to ensure that you get the best speeds.
You will also notice a recent technology that’s developed over the past years called GaN chargers. They use Gallium Nitride in place of traditional Silicon semiconductors, hence the name.
The biggest advantages to GaN chargers are being smaller and more portable, being able to deliver higher power levels with some being able to deliver 100W or more, being more efficient, having multiple USB ports, and being compatible with most fast charging protocols including USB PD.

If you’re using your smartphone while charging, especially for resource-intensive tasks, it might slow down the charging process since some of the power is being used to run the device rather than charge the battery.
Smartphone charging speed is a multidimensional concept influenced by charging technology, charger output power, battery capacity, health, software optimizations, cable quality, and usage during charging.
By understanding these factors, users can make informed decisions to ensure their smartphones are charged efficiently without compromising their longevity.

While faster charging is undoubtedly convenient, it’s important to strike a balance between speed and battery health.
Extremely high charging speeds without proper cooling mechanisms can generate heat and potentially affect battery lifespan. Manufacturers often try to strike a balance between fast charging and maintaining battery health.

YugaTech.com is the largest and longest-running technology site in the Philippines. Originally established in October 2002, the site was transformed into a full-fledged technology platform in 2005.
How to transfer, withdraw money from PayPal to GCash
Prices of Starlink satellite in the Philippines
Install Google GBox to Huawei smartphones
Pag-IBIG MP2 online application
How to check PhilHealth contributions online
How to find your SIM card serial number
Globe, PLDT, Converge, Sky: Unli fiber internet plans compared
10 biggest games in the Google Play Store
LTO periodic medical exam for 10-year licenses
Netflix codes to unlock hidden TV shows, movies
Apple, Asus, Cherry Mobile, Huawei, LG, Nokia, Oppo, Samsung, Sony, Vivo, Xiaomi, Lenovo, Infinix Mobile, Pocophone, Honor, iPhone, OnePlus, Tecno, Realme, HTC, Gionee, Kata, IQ00, Redmi, Razer, CloudFone, Motorola, Panasonic, TCL, Wiko
Best Android smartphones between PHP 20,000 - 25,000
Smartphones under PHP 10,000 in the Philippines
Smartphones under PHP 12K Philippines
Best smartphones for kids under PHP 7,000
Smartphones under PHP 15,000 in the Philippines
Best Android smartphones between PHP 15,000 - 20,000
Smartphones under PHP 20,000 in the Philippines
Most affordable 5G phones in the Philippines under PHP 20K
5G smartphones in the Philippines under PHP 16K
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2024
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2023
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2022
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2021
Smartphone pricelist Philippines 2020